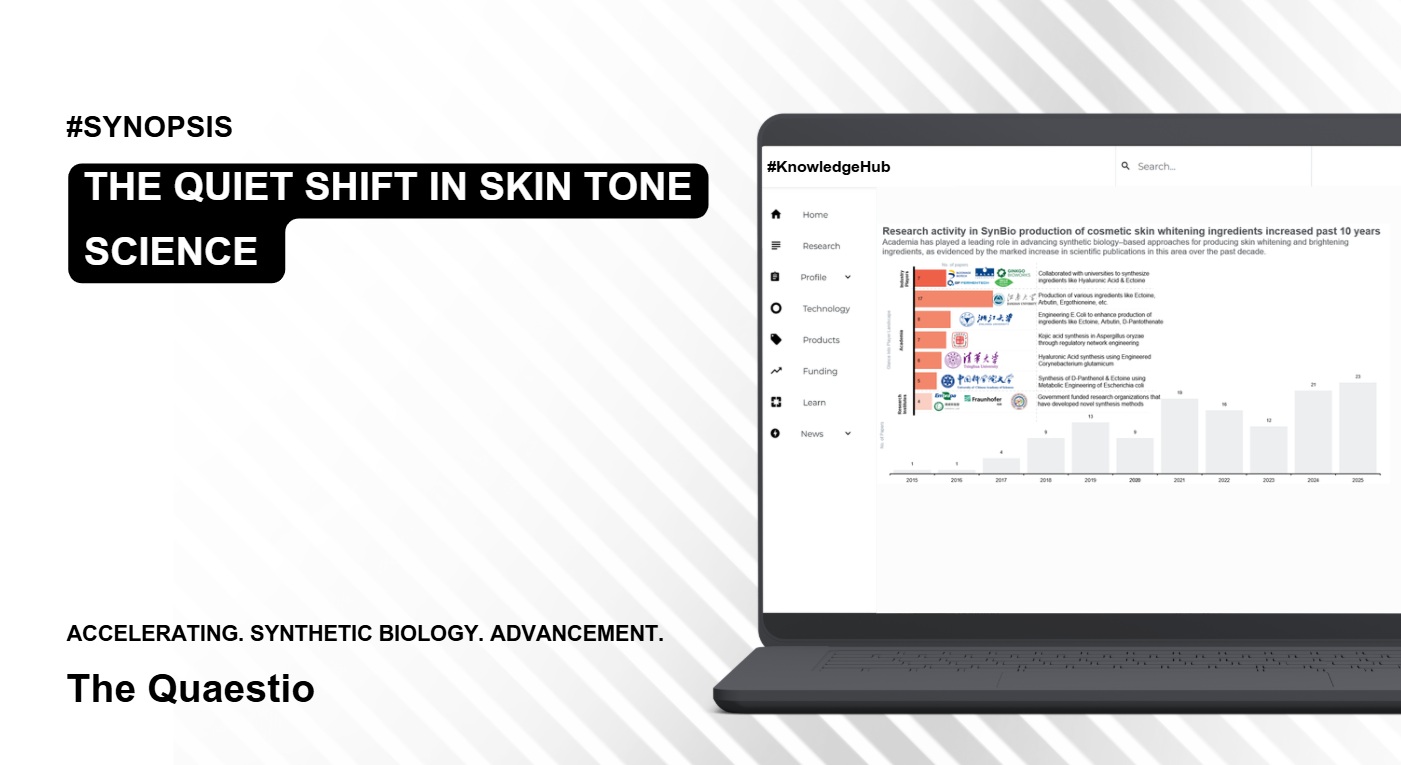
The Quiet Shift in Skin Tone Science
LATEST RESEARCH
LATEST HUB NEWS

Hepta, a biotechnology company using transformer-based AI to decode the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) epigenome and detect organ-specific signals of chronic disease, today announced the creation of an unparalleled multi-omic atlas of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) in collaboration with Duke University. This work builds on Hepta’s expanded cfDNA studies with Mainz University and Akero Therapeutics’ Phase 3 clinical trial program, further strengthening the company’s partnerships across academic and clinical research.
4 months ago Technology Development

Hepta, a biotechnology company using transformer-based AI to read the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) epigenome and detect organ-specific signals of chronic disease, today emerged from stealth with $6.7 million in seed funding led by Felicis Ventures and Illumina Ventures, with participation from SeaX Ventures, Alumni Ventures, and AME Cloud Ventures. The company also revealed clinical data showing its AI-powered epigenetics platform can identify patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, formerly known as NASH) with significant fibrosis with a diagnostic AUC of 0.86, cutting false positives threefold compared to standard blood tests.
4 months ago Investment

Form Bio partnered with Weill Cornell Medicine to apply AI-driven vector design and gene editing for developing therapies that lower Alzheimer’s disease risk in patients with high-risk genetic variants, marking the first phase of a multi-step clinical translation program.
4 months ago Collaboration
The University of Liverpool and CyanoCapture Ltd partnered to develop carboxysome-based targeted drug delivery systems by combining cyanobacteria engineering, peptide expression, and CRISPR-based molecular tools with scalable biomanufacturing to create protein nanocage platforms for biopharmaceutical applications.
4 months ago Collaboration
LATEST HUB PATENTS

Recombinant humanized type III collagen with a triple-helix structure, built from low-immunogenic, high-activity fragments, is efficiently expressed in engineered bacteria at high yield.
Cosmetics

A freckle-removing composition with recombinant humanized collagen linked between two functional fragments of type III collagen and histidine, providing low-irritation skin whitening.
Cosmetics

Recombinant type VII collagen with 2–100 repeats of GLPGAKGEKGAP, expressed in Pichia pastoris with up to 17.3 g/L yield, enhances autophagy and delivers anti-wrinkle effects.
Cosmetics
Synthetic Biology

Recombinant type III collagen, engineered from the human ?1 strand gene and produced in Pichia pastoris offers higher yield for skin regeneration and repair.
Cosmetics
LATEST HUB PAPER

Researchers developed a collagen-like protein, S1552, that is directed into the periplasm of E. coli, where it strengthens the cell barrier and improves resistance to stressors like salt, pH extremes, antibiotics, and heavy metals, with potential use in other bacteria
6 months ago Synthetic Biology

The study introduces antisense RNA (asRNA)-mediated sequestration as a novel mechanism to improve inverting genetic logic gates by co-expressing asRNAs with mRNAs to enhance repression through additional feedback, thereby steepening dose–response curves, reducing OFF-state leakage, and enabling tunable logic transitions for constructing robust combinational circuits; results: improved gate sharpness and reduced leakage.
10 months ago Synthetic Biology

This study presents an automated one-step multigene assembly method that leverages optimized in vivo homologous recombination within a shuttle vector to efficiently construct expression-tunable multigene libraries, with the process miniaturized for high-throughput applications, successfully enabling rapid and parallel gene assembly in a biofoundry setting.
10 months ago Synthetic Biology

This study introduces the Array Assembler, a user-friendly computational tool that streamlines the design of oligonucleotides for assembling large crRNA arrays from user-defined spacer sequences, addressing the complexity and error risks in multitarget CRISPR experiments and enabling rapid, reliable construction of crRNA arrays for diverse genomic perturbation applications.
10 months ago Synthetic Biology
UPDATED PROFILES (DEVELOPERS)
| Name | Industry Tag | Product Tag | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Arc Institute | Medical |
||
 |
EntoZyme | Agriculture |
BSF derived Feeds |
|
 |
Galy | Textile |
Literally Cotton |
NEW PROFILES (DEVELOPERS)
| Name | Industry Tag | Product Tag | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Nutropy | Food |
||
 |
Hepta | |||
 |
Sarvatgc Technologies | Cosmetics |
||
 |
Osmania University | |||
 |
National Institute of Ocean Technology | Cosmetics |
My Followed Profiles
| Name | Type | Country | |
|---|---|---|---|
| You have to login to see followed profiles... | |||
NEW PRODUCT PROFILES
| Name | Product Name | Sub Type | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
LipoTrue | Cellaigie™ | Active Ingredients |

|
Maypharm | SKINCOLLA | Active Ingredients |

|
Uniproma | Arelastin® W | Active Ingredients |

|
Uniproma | RJMPDRN® REC / Sodium DNA | Active Ingredients |

|
Caldera + Lab | The Hydro Layer | Active Ingredients |